
Signal proteins secreted from the ventral and dorsal sides of the neural tube act as opposing morphogens, causing neurons born at different dorsoventral levels to express different gene regulatory proteins ( Figure 21-94). The diagrams are based on reconstructions from sections of the cerebral cortex of a monkey (part (more.) Before sending out axons and dendrites, newborn neurons often migrate from their birthplace and settle in some other location. In the third and final phase, which continues into adult life, the connections are adjusted and refined through interactions among the far-flung components in a way that depends on the electrical signals that pass between them. The next phase involves a type of morphogenesis unique to the nervous system: axons and dendrites grow out along specific routes, setting up a provisional but orderly network of connections between the separate parts of the system. Thus, in the first phase of neural development ( Figure 21-90), the different parts develop according to their own local programs: neurons are born and assigned specific characters according to the place and time of their birth, under the control of inductive signals and gene regulatory mechanisms similar to those we have already discussed for other tissues of the body. The components of a typical nervous system-the various classes of neurons, glial cells, sensory cells, and muscles-originate in a number of widely separate locations in the embryo and are initially unconnected. The black objects are neurons the thin lines are axons and (more.)
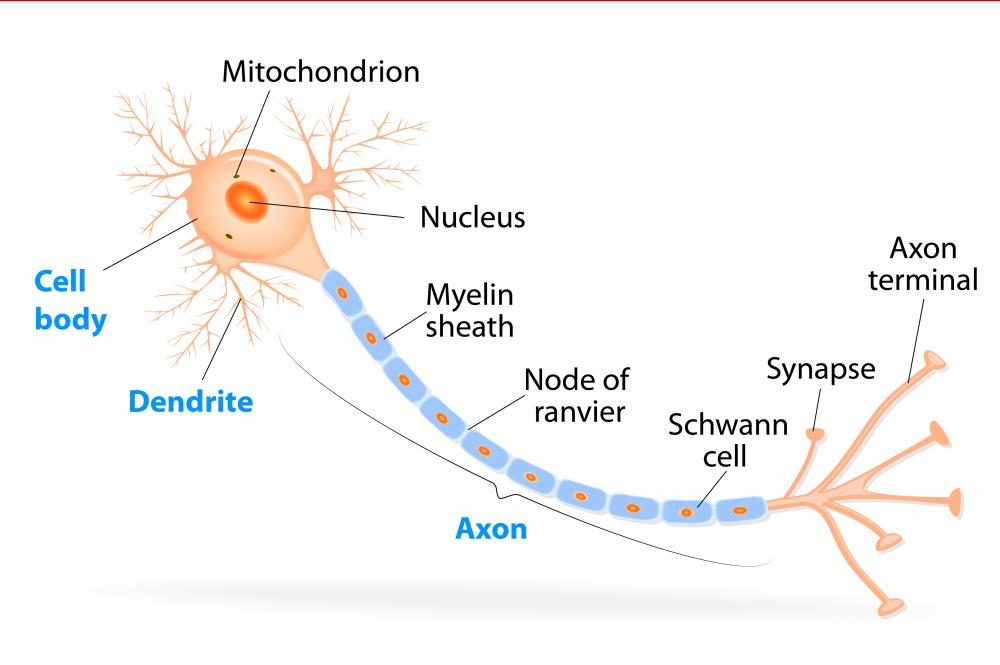

This drawing depicts a section through a small part of a mammalian brain-the olfactory bulb of a dog, stained by the Golgi technique. The complex organization of nerve cell connections. The precision required is not so great as in a man-made computer, for the brain performs its computations in a different way and is more tolerant of vagaries in individual components but the brain nevertheless outstrips all other biological structures in its organized complexity. The problem is formidable: the human brain contains more than 10 11 neurons, each of which, on average, has to make connections with a thousand others, according to a regular and predictable wiring plan. The central challenge of neural development is to explain how the axons and dendrites grow out, find their right partners, and synapse with them selectively to create a functional network ( Figure 21-89). A neuron is extraordinary above all for its enormously extended shape, with a long axon and branching dendrites connecting it through synapses to other cells ( Figure 21-88).

Their structure is like that of no other class of cells, and the development of the nervous system poses problems that have no real parallel in other tissues. Nerve cells, or neurons, are among the most ancient of all specialized animal cell types.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
